Imagine you have a list of 10,000 transactions - all the buys, sells, and transfers that happened in one block of Bitcoin. Now imagine you need to prove one of those transactions is real, without downloading all 10,000. That’s where Merkle trees come in. They’re not flashy, but they’re what keep blockchains fast, light, and secure.
How Merkle Trees Work
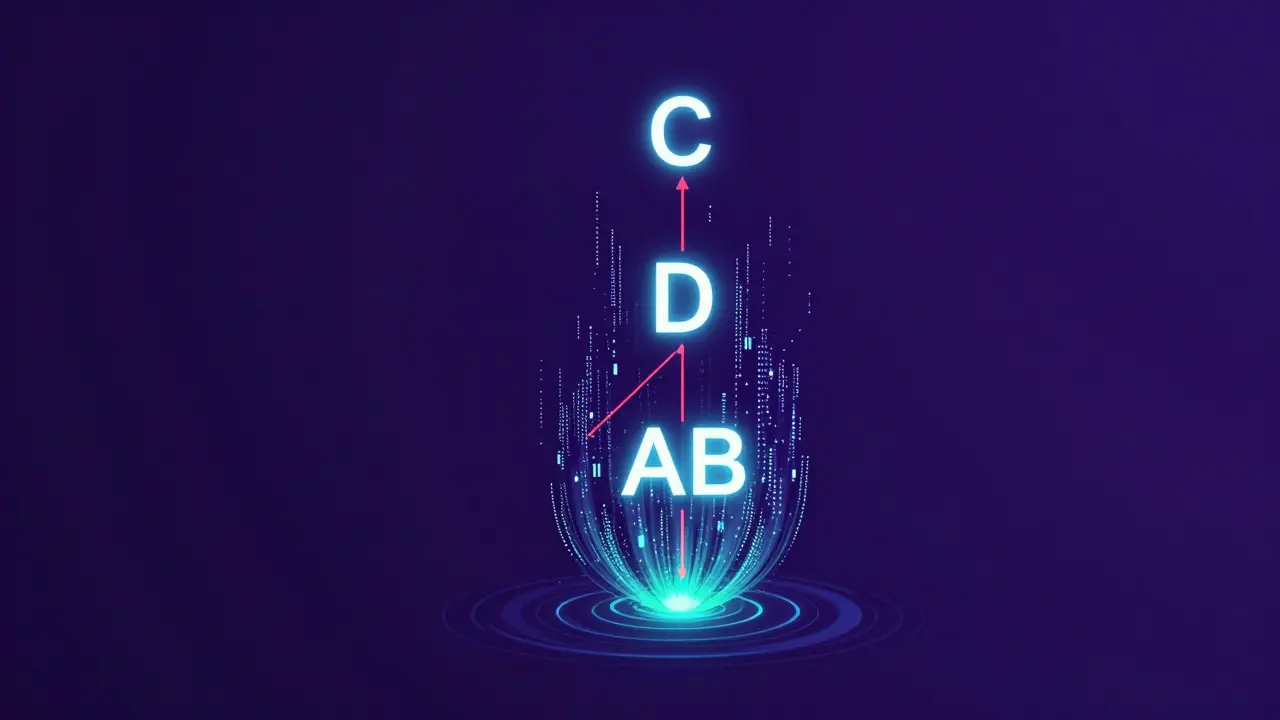
A Merkle tree is a binary tree made of hashes. Each leaf node holds the hash of a single transaction. Every node above it combines the hashes of its two children into one new hash. You keep doing this until you reach the top - the Merkle root. That one hash represents everything below it.Let’s say you have four transactions: T1, T2, T3, T4. You hash each one:
- Hash(T1) = A
- Hash(T2) = B
- Hash(T3) = C
- Hash(T4) = D
Then you pair them up and hash the pairs:
- Hash(A + B) = AB
- Hash(C + D) = CD
Finally, you hash those two together:
- Hash(AB + CD) = Merkle Root
This root gets stored in the block header. Every full node in the network knows this root. If even one transaction changes - say, someone tries to alter T3 - the whole chain of hashes breaks. The root won’t match. The block gets rejected.
Why This Matters for Blockchain
Without Merkle trees, every node would have to store every single transaction in full. That’s not practical. Bitcoin blocks can hold over 5,000 transactions. Ethereum often hits 20,000+. Storing all of them raw would make blockchain nodes huge, slow, and expensive to run.Merkle trees solve this by compressing thousands of transactions into one 32-byte hash. The entire block header - including timestamp, previous block hash, nonce, and Merkle root - fits in less than 1 kilobyte. That’s why your phone wallet can verify a transaction without downloading the whole blockchain.
It’s not magic. It’s math. And it’s brilliant.
Merkle Proofs: Proving Something Exists Without Showing Everything
Here’s the real power: you don’t need all the data to prove a transaction is part of a block. You just need a short path - a Merkle proof.Let’s say you want to prove T3 is in the block. You don’t need T1, T2, or T4. You only need:
- The hash of T3 (C)
- The hash of T4 (D) - because it’s T3’s sibling
- The hash of AB - the other branch
You take C and D, hash them together to get CD. Then hash CD with AB to get the Merkle root. If it matches the one in the block header, T3 was definitely there. That’s just three hashes - 96 bytes - to prove one transaction out of 10,000.
This is how lightweight wallets (SPV wallets) work. They don’t store full blocks. They just ask a full node: “Is this transaction in block #800,000?” The full node sends back the Merkle proof. The wallet checks it. Done. No download. No fuss.
What Happens When There’s an Odd Number of Transactions?
Merkle trees need pairs. If you have 5 transactions, you can’t pair the last one. So the system duplicates it. That’s right - the fifth transaction gets hashed twice.It’s not a flaw. It’s a design choice. It keeps the tree balanced and predictable. The duplicate doesn’t change anything. It’s still cryptographically secure. You can’t fake it. You can’t reverse it. The hash of a duplicated transaction is still unique to that exact data.
Some people think this is wasteful. But the cost is tiny. One extra hash per block. For a system moving billions of dollars daily, that’s nothing.
Limitations - What Merkle Trees Can’t Do
Merkle trees are great at proving something is there. But they’re bad at proving something is not there.If you ask: “Is transaction X in this block?” - easy. You get a proof.
If you ask: “Is transaction X not in this block?” - you’re stuck. You’d have to download the whole block and check every transaction. No shortcut.
That’s why Ethereum uses something called a Merkle Patricia tree for account states. It’s a modified version that can handle key-value lookups efficiently. It lets you prove not just that a transaction happened, but that an account had a specific balance at a certain time.
Another issue: if you add a new transaction, you have to rebuild the whole tree from the bottom up. That’s why miners batch transactions before building a block. They don’t add one at a time - they build the tree once, then seal it.

Real-World Use Cases
Bitcoin uses Merkle trees in every block. Every single one. Since 2009. Billions of transactions verified. Zero failures.Ethereum uses them too - but differently. Its Merkle Patricia tree tracks account balances, smart contract code, and storage. That’s why you can check your ETH balance without syncing the whole chain.
Layer 2 solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum rely on Merkle proofs to submit batches of transactions to Ethereum. They compress thousands of off-chain transactions into one Merkle root. Then they prove to Ethereum that those transactions are valid - without sending all the data.
Even non-blockchain systems use Merkle trees. Git uses them to track file changes. Dropbox uses them to detect file duplicates. The idea is old, but it’s still the best tool for the job.
What’s Next for Merkle Trees?
Researchers are already working on next-gen versions. Sparse Merkle trees let you prove something is absent - a big step forward. Quantum-resistant hash functions are being tested to protect against future attacks.Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are combining with Merkle trees to create privacy layers. Imagine proving you have enough funds to make a payment - without revealing how much you have. That’s the future.
But here’s the thing: even with all this innovation, the core idea hasn’t changed. Hashes. Trees. Roots. It’s still the same elegant system Ralph Merkle designed in 1979.
Why You Should Care
You might never see a Merkle tree. But every time you send crypto, check your balance, or use a wallet app - it’s working behind the scenes. It’s what lets your phone verify a Bitcoin transaction in under a second. It’s what keeps the network running without needing a supercomputer.Without Merkle trees, blockchain would be slow, bloated, and unusable for everyday people. They’re the quiet engine that makes decentralization possible at scale.
They’re not the flashiest part of crypto. But they’re one of the most important.
Are Merkle trees only used in Bitcoin?
No. While Bitcoin popularized them, nearly every major blockchain - Ethereum, Litecoin, Binance Chain, Solana - uses Merkle trees or variations. Ethereum uses Merkle Patricia trees for account states. Layer 2 networks like Polygon and zkSync rely on Merkle proofs to batch transactions. They’re a standard tool in blockchain design.
Can Merkle trees be hacked?
Not if the hash function is secure. Bitcoin uses SHA-256, which is still unbroken after 15+ years. The security comes from two things: cryptographic hash functions (you can’t reverse them) and the tree structure (changing one transaction changes the root). To fake a Merkle proof, you’d need to break SHA-256 - which no one has done. The system is mathematically sound.
Do I need to understand Merkle trees to use crypto?
No. Most users never see them. Wallets and apps handle everything automatically. But if you want to know how your transactions are verified, or why your phone can check your balance without downloading the whole blockchain, understanding Merkle trees gives you real insight into how the system works under the hood.
Why not just store all transactions in the block header?
Because it would be impossible. A Bitcoin block can have 5,000+ transactions. Each transaction is 200-500 bytes. That’s over 1MB of raw data just for transactions - and that’s before adding timestamps, signatures, and metadata. The block header is kept under 1KB. Merkle trees compress all that data into one small hash. That’s the only way the system scales.
How do Merkle trees help with blockchain scalability?
They reduce what each node needs to store and verify. Full nodes keep transaction data in local databases (like LevelDB), but only the Merkle root is stored on-chain. Light nodes only download headers and Merkle proofs. This cuts bandwidth and storage by 90%+ compared to storing everything. Layer 2 systems like rollups use Merkle trees to prove thousands of off-chain transactions with one on-chain proof - making the whole network faster and cheaper.

Greg Knapp
December 16, 2025 AT 12:20So basically its just a fancy way to say if one thing changes everything breaks lol
Shruti Sinha
December 16, 2025 AT 12:40This is an exceptionally clear explanation. The structure of the Merkle tree ensures integrity through cryptographic hashing, and the efficiency of verification scales logarithmically rather than linearly. A brilliant application of computer science fundamentals.
Heather Turnbow
December 18, 2025 AT 00:38I appreciate how you emphasized the quiet importance of Merkle trees. Most people focus on mining or consensus, but without this elegant compression mechanism, blockchain wouldn't be accessible to everyday users. It’s the invisible architecture that makes decentralization practical.
Jesse Messiah
December 19, 2025 AT 03:01Man, this made so much sense. I always thought blockchains were just a bunch of hashes floating around, but seeing how the tree works like a digital family tree of transactions? That’s genius. Thanks for breaking it down like this.
Elvis Lam
December 19, 2025 AT 07:57You missed the point about Merkle proofs being the reason SPV wallets exist. Without them, mobile crypto apps would be useless. The entire lightweight client model relies on this. This isn't just theory-it's what lets your phone verify transactions in 0.3 seconds. If you don't get this, you don't get blockchain.
Jonny Cena
December 19, 2025 AT 13:32Great breakdown. I love how you explained the odd-numbered transaction handling-it’s such a simple fix that keeps everything stable. Also, the part about Git and Dropbox using the same idea? That’s wild. It shows how foundational this is beyond crypto.
Sue Bumgarner
December 20, 2025 AT 07:13Everyone in the world uses this except China. They have their own blockchain tech-way better. This Merkle thing is just American crypto propaganda. We don't need it. We have state-approved ledgers that are faster and more secure.
Emma Sherwood
December 21, 2025 AT 11:38As someone who grew up in a country where digital infrastructure was nonexistent 20 years ago, seeing this elegant solution emerge from open-source collaboration gives me chills. It’s not just tech-it’s a global language of trust. And yes, even my grandma uses a wallet that relies on this. That’s power.
Amy Copeland
December 21, 2025 AT 13:42Oh wow. A whole post about how hashes work. Did you get this from a 2012 Bitcoin forum? I mean, it’s cute. Like explaining wheels to someone who’s never seen a cart. But it’s 2024-we’ve moved on to zk-SNARKs and recursive proofs. This is blockchain kindergarten.
Timothy Slazyk
December 22, 2025 AT 11:26What’s fascinating isn’t just the structure-it’s what this implies about epistemology. We no longer need to trust a central authority to verify truth. We trust the math. And the math, when properly implemented, cannot lie. This isn’t just a data structure. It’s a new way of knowing. The Merkle root is the modern oracle. And yet, we still treat it like a tool rather than a revolution.
Madhavi Shyam
December 24, 2025 AT 06:47Merkle root = commitment. Merkle proof = non-interactive zero-knowledge witness. SPV = light client validation. This is core consensus layer design. You’re not just verifying tx-you’re validating state inclusion without full node sync.
Mark Cook
December 24, 2025 AT 09:39Wait so if I change one letter in a transaction… the whole thing breaks? 😱 That’s like if I misspell ‘cat’ and suddenly the whole dictionary explodes. Cool. 🤯
Jack Daniels
December 25, 2025 AT 15:49I read this three times. Still don’t get it. But I like the word ‘hashes’. Feels powerful. Like magic spells. I’m just here for the vibes.
Bradley Cassidy
December 25, 2025 AT 23:02Yo this is legit fire. I was like ‘meh merkle tree’ but now I’m seeing it like a digital family tree where every cousin’s name is a hash and if one cousin lies, the whole reunion falls apart 😂 Thanks man, I finally get it. Also typo: ‘hashes’ is now ‘hashez’ in my brain and I’m not sorry.
Samantha West
December 27, 2025 AT 06:21The elegance of this system speaks to the divine order of mathematics. In a world of chaos, the Merkle tree stands as a testament to rationality. One cannot help but wonder-did Merkle glimpse the mind of God when he conceived this? Or was it merely the product of human ingenuity, limited yet luminous?
And yet, we still cling to SHA-256. What if quantum machines unravel its foundations? What then? Do we rebuild the temple? Or do we accept that all structures, even cryptographic ones, are temporary?
Perhaps the true Merkle root is not a hash-but the collective trust we place in abstraction itself.